appendicel torsion testes|what is a testicular appendage : traders Torsion of the appendix testis (occasionally called torsion of the hydatid of Morgagni) is the most common cause of an acute painful hemiscrotum in a child. The . WEBStripchat.com is an international adult website and social network featuring free live-streamed webcam performances, often including nudity and sexual activity, through .
{plog:ftitle_list}
WEBPortal O Tempo. Loterias. Artigo. LOTERIAS. Resultado da Lotofácil 2952 deste sábado (11/11) O prêmio estimado é de R$ 1,7 milhão; as apostas podem ser feitas até as 19h. .
The appendix testis is a small appendage of normal tissue that is usually located on the upper portion of the testis. The appendix epididymis is a small appendage on the top of the epididymis (a tube-shaped structure connected to the . Torsion of the appendix testis (occasionally called torsion of the hydatid of Morgagni) is the most common cause of an acute painful hemiscrotum in a child. The . Differentiate between torsion of the appendix testis and other causes of acute scrotal pain, such as testicular torsion or epididymo-orchitis. Assess the severity and . Appendix testis torsion is a condition that affects the testes of the male reproductive system. This article looks at the symptoms and causes of this condition and .
what is a testicular appendage
torsion appendix testis ultrasound
Torsion of the appendix testis is a twisting of a vestigial appendage that is located along the testicle. This appendage has no function, yet more than half of all boys are born with one. . An appendix testis is a normal piece of tissue on the testicle and is present in most people designated male at birth. Appendix testis torsion (twisting) is common between the .
Torsion of testicular appendages can result in the clinical presentation of acute scrotum. Two such appendages are the appendix testis, a remnant of the paramesonephric (müllerian) duct,.
When the appendix testis undergoes torsion, a hard, tender nodule may be palpable on the upper pole of the testicle, and a blue discoloration referred to as the “blue dot .
Testicular torsion is a clinical diagnosis, and patients typically present with severe acute unilateral scrotal pain, nausea, and vomiting. Physical examination may reveal a high-riding. Two testicular appendages can undergo torsion and become symptomatic: the appendix testis and the appendix epididymis. The appendix testis, sometimes called . The appendix testis, sometimes called hydatid of Morgagni, is a vestigial remnant of the Mullerian duct and is present in 76% to 83% of testes. When present, it is located on the superior pole of the testicle between the testis and epididymis and is the most common testicular appendage to undergo torsion.
Testicular torsion occurs when the testicle rotates on the spermatic cord, which brings blood to the testicle from the abdomen. If the testicle rotates several times, blood flow to it can be entirely blocked, causing damage more quickly. It's not clear why testicular torsion occurs. Most males who get testicular torsion have an inherited trait .
Torsion of the appendix testis (occasionally called torsion of the hydatid of Morgagni) is the most common cause of an acute painful hemiscrotum in a child. The appendix testis is located at the upper pole of the testis (between the .Testicular torsion, torsion of appendix testis, & epididymitis 39. the emergency department with a 2-day history of scrotal pain and was ultimately determined to have testicular torsion. He was initially diagnosed with epididymitis based on the .The appendix testis (or hydatid of Morgagni) is a vestigial remnant of the Müllerian duct, . If clinical suspicion is high for the serious differential diagnosis of testicular torsion, a surgical exploration of the scrotum is warranted. Torsion of the appendix of testis occurs at ages 0–15 years, with a mean at 10 years, which is similar . Two testicular appendages can undergo torsion and become symptomatic: the appendix testis and the appendix epididymis. The appendix testis, sometimes called hydatid of Morgagni, is a vestigial remnant of the Mullerian duct and is present in 76% to 83% of testes. [2]
Expert opinion in a review article notes there is a 4–8 hour window for surgical management before permanent ischaemic damage to the testicle occurs, with potentially decreased fertility and/or the need for orchidectomy if there is a necrotic or non-viable testicle [Sharp, 2013]. Torsion of the appendix testis can usually be managed non . Testicular torsion occurs when a testis torts on the spermatic cord resulting in the cutting off of blood supply. . torsion of the epididymal appendix. this is more of a clinical differential diagnosis; testis and epididymis are normal; small pedunculated avascular nodule may be seen (very tender) Testicular torsion symptoms. The typical symptom of torsion of the testicle (testis) is severe pain that develops quickly - within a few hours, often much more quickly.
torsion appendix testis
Purpose Torsion of the appendix testis or epididymis is a cause of acute scrotum in children. Ultrasonography with color Doppler is the first-choice modality for diagnosis. However, this method requires skill and experience to make a diagnosis with confidence. Recently, contrast-enhanced ultrasonography for diagnosis in various fields has been reported. However, to our .
The appendix testis is a small piece of tissue that is usually located on the upper part of the testis. The appendix epididymis is a small appendage located at the top of the epididymis (tube-shaped structure that connects to the testicle). Torsion means that this tissue has twisted. Because this structure serves no purpose, torsion does not .Appendix testis and appendix epididymis can torse Most common between 7-14yr; No affect on fertility or surrounding structures; Clinical Features. Scrotal pain. Milder and more gradual onset compared to testicular torsion; Localized to one point of testicle; Physical exam Hard, tender 2-3mm nodule at upper pole of testicle;
Testicular Appendage Torsion. Testicular appendage torsion is the twisting of a small piece of tissue above a testicle. The appendage doesn’t have a function in the body. But it can twist and cause pain and swelling that gets worse over time. It's not the same as testicular torsion.
Torsion of any of the four testicular appendages [appendix testis (remnant of paramesonephric duct), appendix epididymis (remnant of the mesonephric duct), paradidymis (organ of Giraldes) and vas aberrans (organ of Haller)] may present with an acute scrotum, especially in children. 25 The appendix testis is usually located at the superior . Surgical treatment of torsion of the appendix testis is not mandatory but hastens recovery. Each year, testicular torsion affects one in 4,000 males younger than 25 years. Early diagnosis and . Torsion af appendix testis - Morgagnis hydatid, som udgør en embryonal rest af den Müllerske gang Hos børn er torsion af appendix testis den hyppigste årsag til akut skrotum ; Tilstanden er vanskelig at adskille fra testistorsion, epididymitis og orchitis; I nogle tilfælde kan ømheden og smerterne isoleres til et punkt på testiklen . What is torsion of the appendix testis? The testicular appendage is a small amount of normal tissue, usually located on the upper part of a testis, left over from the time of testicular fetal development. Most boys will have it present at birth. Twisting of this appendix testis is called torsion of the appendix testis and it tends to occur in .
Testicular torsion is an emergency. It requires immediate referral to a surgeon; Surgical evaluation should be undertaken in all cases where testicular torsion cannot be confidently excluded; Ultrasound should only be considered in selected cases of testicular pain, after surgical assessment, to avoid delays in management It is important to distinguish appendix torsion from frank testicular torsion because the treatment for appendix torsion is generally symptomatic while torsion of the testis is a true surgical emergency. Epididymo-orchitis has relatively classic imaging features and may be associated with dysuria due to concomitant urinary tract infection. Look .Background: Torsion of the testicular appendix is the commonest cause of acute scrotum in children. The histological picture of these cases is variable and many show a heavy acute inflammatory cell infiltrate, unlike the response to pure ischaemic necrosis in other organs. The clinical implications and consequences of this associated inflammation are not clear. Methods: . The patient's presentation, including imaging and pathology, is diagnostic of testicular torsion. Testicular infarct following torsion is initially associated with conservation of germ cells; however, as congestion and hemorrhage increase, these cells slough into the lumens of seminiferous tubules and ultimately the entire tubule undergoes .
A diagnosis of testicular torsion should be suspected in any person presenting with acute scrotal pain and/or swelling, before other causes are considered.. Ask about:. Any scrotal pain — the location (including unilateral or bilateral), nature, radiation to surrounding structures, speed of onset, duration, severity, exacerbating factors (such as activity or positional changes).One of the two patients with decreased blood flow had testicular torsion; the other had torsion of the appendix testis. The color Doppler examination showed increased or normal blood flow in 182 . Testicular torsion in newborns and infants. Testicular torsion can occur in newborns and infants, though it's rare. The infant's testicle might be hard, swollen or a darker color. Ultrasound might not detect reduced blood flow to the infant's scrotum, so surgery might be needed to confirm testicular torsion. Treatment for testicular torsion in . Introduction. Testicular torsion occurs when the spermatic cord and its contents twists within the tunica vaginalis, compromising the blood supply to the testicle.. Testicular torsion is a surgical emergency, as without treatment the affected testicle will infarct within hours.Whilst theoretically it can occur at any age, peak incidence is in neonates and .
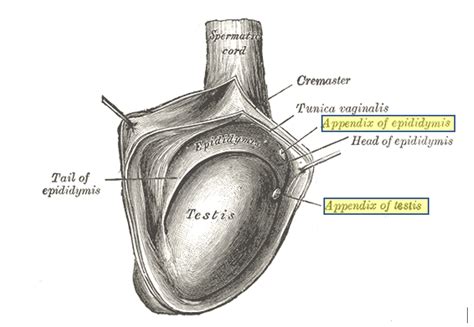
The appendix testis is a small piece of tissue attached to the testicle. It is left over from before birth. It's a normal part of the system that creates female organs. Since it isn't needed in boys, it may disappear. But in many boys it remains attached. It serves no purpose, but it can become twisted (torsion).Mullerian or Wolffian duct remnants (Figure 5). Similar to testis torsion, torsion of the appendix testis or appendix epididymis can also present with the acute onset of scrotal pain and mass. In most cases, however, the testis is palpable and has a normal lie. If encountered early, the
web6 de jan. de 2024 · Tudo sobre o Big Brother Famosos da TVI é aqui no dioguinho. O maior reality show do mundo vai voltar a abrir as portas de sua casa para uma edição especial com caras conhecidas do grande público. TESOURINHO! Vê aqui imagens de Cláudio Ramos no “Big Brother Famosos” (2002) Cláudio Ramos está de regresso ao .
appendicel torsion testes|what is a testicular appendage